Visualizing Real-Time Map Rotation with GPS Coordinates on iOS
Smooth vehicle animations in navigation apps like Uber or Google Maps seem effortless—but under the hood, you're only given discrete GPS coordinates. This post explores how to derive orientation and simulate real-time movement using basic geometry and Swift. The approach is platform-agnostic but demonstrated here using CLLocationCoordinate2D, trigonometric functions like atan, and foundational vector math.
We start by imagining a Cartesian plane. Each time the vehicle moves, it emits a new GPS coordinate: latitude and longitude. These correspond to X and Y.
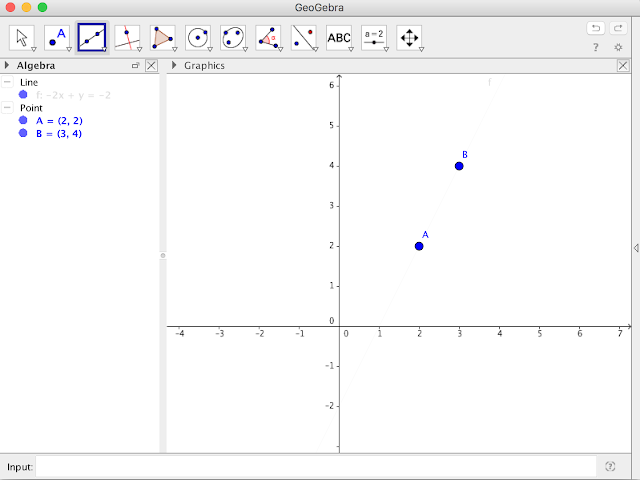
Now, let’s look at two sequential points:
Calculating Direction from Two Coordinates
To compute the heading angle (tilt), use the slope between A and B.
- A₀ = ΔX = xB - xA
- B₀ = ΔY = yB - yA
With these values:
m = tan(α) = ΔY / ΔX
Then, using the arctangent:
α = atan(m)
In Swift, you work with CLLocationCoordinate2D for geographic points. To calculate the angle between two, you do something like this:
This gives the rotation angle (heading) in radians, usable in `CGAffineTransform` or `MKAnnotationView` updates.
Conclusion
By converting coordinate deltas into an angle via atan, you can animate vehicles naturally along routes. The principles remain consistent across platforms and work elegantly in Swift with minor math and trigonometry.